Addressing Potential Nutritional Deficiencies
Plant power nutrition facts – Yo, Medan peeps! Going plant-based is awesome for your health and the planet, but let’s be real – a poorly planned vegan diet can leave you feeling, well, less than awesome. We’re talking potential nutrient gaps that can seriously impact your energy levels and overall well-being. So, let’s dive into how to avoid those pitfalls and make sure your plant-powered life is thriving, not just surviving.
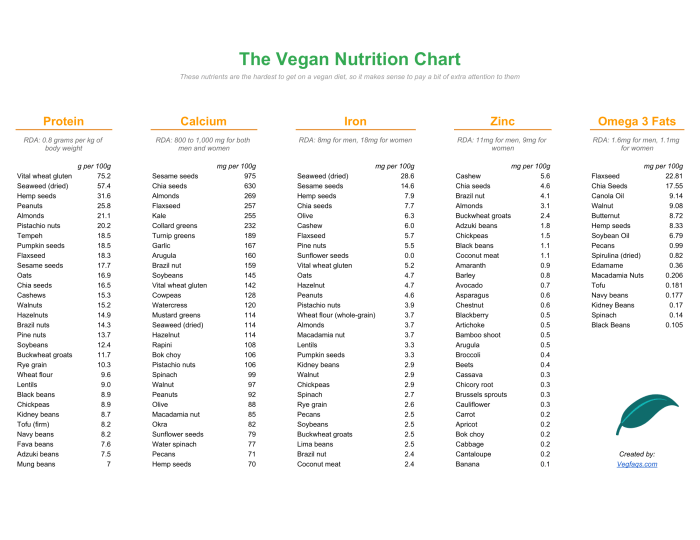
Potential Nutrient Deficiencies in Plant-Based Diets, Plant power nutrition facts
Okay, let’s get down to brass tacks. Some nutrients are trickier to get enough of when you ditch animal products. We’re talking Vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids – the usual suspects. A lack of these can lead to fatigue, weakness, anemia, and even bone problems. But don’t panic! It’s totally manageable with a little planning and know-how.
It’s all about making informed choices and embracing the delicious diversity of the plant kingdom.
Strategies for Ensuring Adequate Nutrient Intake
The key here, my friends, is strategic planning and diversification. It’s not just about eating
- enough* plants; it’s about eating the
- right* plants. For Vitamin B12, fortified foods and supplements are your best bet, as it’s not naturally found in plants. For iron, pair iron-rich plant foods with Vitamin C-rich foods to boost absorption. Think spinach and oranges – a match made in heaven! Calcium can be found in leafy greens, fortified plant milks, and tofu. And for omega-3s, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are your go-to sources.
Remember, a balanced diet is key.
The Importance of Food Diversity
Think of your plate as a vibrant garden, not a monoculture. Variety is the spice of life, and in this case, it’s also the key to preventing deficiencies. Don’t rely on just one or two plant sources for your nutrients. Mix it up! Experiment with different fruits, vegetables, legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds. The more colorful your plate, the better nourished you’ll be.
Plant-based diets offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, often boasting high fiber and antioxidant content. However, even a plant-powered lifestyle needs careful consideration of calorie intake. For a contrasting example of a readily available beverage, you might check the specifics at la colombe cold brew nutrition facts to understand its nutritional profile. Returning to plant power, remember that balanced nutrition is key, regardless of your dietary choices.
Plant-Based Foods Rich in Essential Nutrients
- Vitamin B12: Nutritional yeast, fortified plant milks (soy, almond, oat), B12 supplements.
- Iron: Spinach, lentils, chickpeas, tofu, black beans, fortified cereals.
- Calcium: Kale, collard greens, bok choy, fortified plant milks, tofu (calcium-set).
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, hemp seeds, seaweed.
Practical Application of Plant Power Nutrition: Plant Power Nutrition Facts

Yo, Medan peeps! Let’s ditch the diet drama and get real about plant-based eating. It’s not about deprivation; it’s about delicious, energizing meals that fuel your body and the planet. This section dives into practical ways to build a vibrant, plant-powered lifestyle. We’ll craft a sample meal plan, whip up some tasty recipes, and show you how to smoothly integrate more plants into your everyday grub.
Get ready to level up your eating game!
A Week of Plant-Powered Meals
Planning your meals ahead is key to consistent healthy eating. This sample plan offers variety and flexibility, so feel free to swap things around based on your preferences and what’s fresh at the market. Remember, this is just a starting point – the possibilities are endless!
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Overnight oats with berries and nuts | Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread | Tofu stir-fry with brown rice and broccoli |
| Tuesday | Smoothie with spinach, banana, and almond milk | Quinoa salad with chickpeas, cucumber, and tomatoes | Black bean burgers on whole-wheat buns with sweet potato fries |
| Wednesday | Avocado toast with everything bagel seasoning | Leftover black bean burgers | Vegetable curry with brown rice |
| Thursday | Chia seed pudding with mango and coconut flakes | Salad with grilled halloumi (optional, for extra protein) and mixed greens | Pasta with marinara sauce and vegetables |
| Friday | Fruit salad with Greek yogurt (optional, for extra protein) | Leftover vegetable curry | Pizza with whole-wheat crust, vegetables, and vegan cheese |
| Saturday | Pancakes made with whole-wheat flour and banana | Buddha bowl with roasted vegetables and tahini dressing | Homemade veggie burgers on whole wheat buns with a side salad |
| Sunday | Breakfast burrito with scrambled tofu, black beans, and salsa | Leftover veggie burgers | Lentil Shepherd’s Pie with mashed sweet potatoes |
Delicious and Nutritious Plant-Based Recipes
Let’s get cooking! Here are a couple of easy-to-make, flavour-packed recipes to get you started.
Tofu Scramble
This is a fantastic protein-packed breakfast or brunch option. Simply crumble firm or extra-firm tofu into a pan, sauté with chopped onions, bell peppers, and your favorite spices (turmeric, cumin, paprika are great choices). Season with salt and pepper to taste. Serve with toast or alongside some roasted potatoes for a heartier meal.
Lentil Soup
This hearty soup is packed with protein and fiber. Sauté diced carrots, celery, and onions in olive oil. Add red lentils, vegetable broth, diced tomatoes, and spices (cumin, coriander, turmeric). Simmer until lentils are tender. Blend a portion for a creamier texture, if desired.
Gradually Incorporating Plant-Based Foods
Don’t feel pressured to go fully vegan overnight. Start small and build up gradually. Try swapping one meat-based meal a week with a plant-based alternative. Gradually increase your intake of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. Experiment with different plant-based protein sources like tofu, tempeh, lentils, and beans.
It’s a journey, not a race!
Comparing Plant-Based Protein Sources
This table shows the approximate protein content (per 100g) of some popular plant-based protein sources. Remember that these are averages and can vary based on factors like the specific type of food and growing conditions.
| Food | Protein (g) | Other Nutritional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Tofu | 8-12 | Good source of iron and calcium |
| Lentils | 25-28 | High in fiber and iron |
| Chickpeas | 19-20 | Good source of fiber and folate |
| Quinoa | 14-15 | Complete protein, good source of iron and fiber |
FAQ Overview
What are the best sources of Vitamin B12 for plant-based eaters?
Fortified nutritional yeast, B12 supplements, and tempeh are excellent sources of vitamin B12 for those following a plant-based diet.
How can I ensure I’m getting enough iron on a plant-based diet?
Consume iron-rich foods like lentils, spinach, and tofu alongside vitamin C-rich foods to enhance iron absorption. Consider a blood test to monitor your iron levels.
Are there any risks associated with a poorly planned plant-based diet?
Yes, a poorly planned plant-based diet can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. Careful planning and supplementation, where necessary, are crucial.
How can I transition to a plant-based diet gradually?
Start by incorporating more plant-based meals into your week, gradually reducing your consumption of animal products. Focus on adding plant-based foods rather than solely restricting animal products.
