Health Implications and Considerations

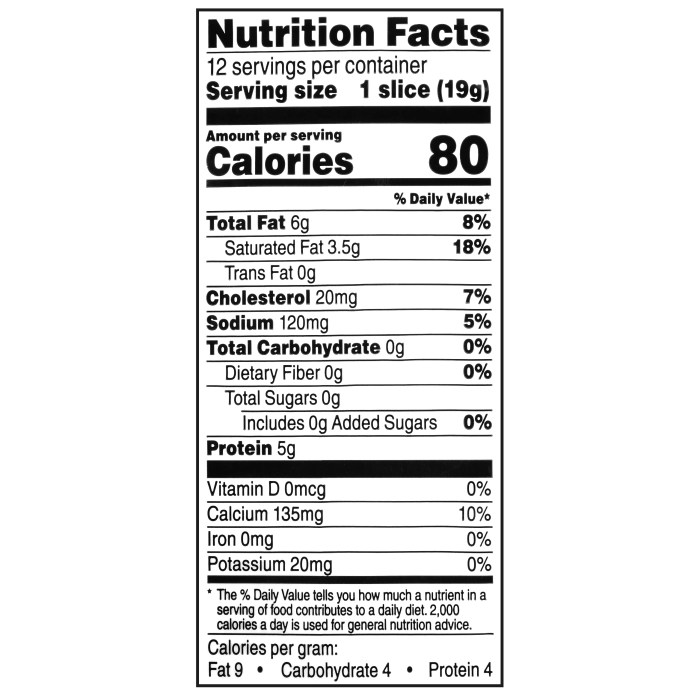
Nutrition facts american cheese – American cheese, a ubiquitous staple in many diets, presents a complex nutritional landscape. Its convenient form and familiar taste often overshadow a closer examination of its potential health impacts, both positive and negative. Understanding the interplay of its components—sodium, saturated fat, and potential allergens—is crucial for informed consumption. The processing methods employed also significantly influence the final nutritional profile and, consequently, the cheese’s effects on health.
Regular consumption of American cheese can contribute to a higher sodium intake, potentially exacerbating hypertension in susceptible individuals. The high saturated fat content raises concerns about its contribution to elevated cholesterol levels and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Moreover, milk proteins, a primary component of American cheese, can trigger allergic reactions in individuals with milk allergies or lactose intolerance.
Conversely, American cheese does provide a source of calcium, essential for bone health, and it contributes to protein intake, vital for building and repairing tissues.
Sodium Content and Cardiovascular Health
The high sodium content in American cheese is a significant concern. One slice can easily contain a substantial portion of the recommended daily sodium intake. Excessive sodium consumption is strongly linked to high blood pressure, increasing the risk of stroke and heart disease. Individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions or a family history of hypertension should monitor their American cheese consumption carefully and consider lower-sodium alternatives.
For example, a study published in the “Journal of the American Medical Association” demonstrated a clear correlation between high sodium intake and increased cardiovascular mortality.
Saturated Fat and Cholesterol Levels
American cheese’s relatively high saturated fat content poses another potential health risk. Saturated fats can raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, contributing to the formation of plaque in arteries and increasing the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. While some saturated fat is necessary for bodily functions, excessive intake should be avoided. Dietary guidelines recommend limiting saturated fat intake to minimize these risks.
Choosing leaner protein sources and incorporating more unsaturated fats from sources like olive oil and avocados can help balance the dietary intake.
Right, so you’re checking the nutrition facts american cheese, yeah? Thing is, that processed stuff ain’t always the healthiest. For a proper nutritional breakdown, though, check out joella’s nutrition facts – it’s a proper eye-opener compared to that cheese. Then you can make a proper judgement on your American cheese cravings, innit?
Impact of Processing Methods
The processing methods used in American cheese production significantly affect its nutritional value and potential health effects. Different methods influence the fat content, sodium levels, and the presence of additives. For instance, cheeses made with higher-fat milk will naturally have a higher saturated fat content. The addition of sodium during processing further contributes to its high sodium content.
Comparative Analysis of Processing Methods
| Processing Method | Sodium Content (mg/slice) | Saturated Fat (g/slice) | Potential Health Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Process (High Heat, Additives) | ~200-300 | ~4-6 | Increased risk of hypertension and high cholesterol |
| Reduced-Sodium Process | ~100-150 | ~4-6 | Lower risk of hypertension, but still high in saturated fat |
| Lower-Fat Process | ~200-300 | ~2-3 | Lower risk of high cholesterol, but still high in sodium |
| Artisan/Cheddar-Style (Minimal Processing) | ~100-200 | ~3-5 | Generally lower in sodium and saturated fat than standard process |
Consumer Perceptions and Marketing
American cheese, a ubiquitous presence in refrigerators across the nation, enjoys a complex relationship with consumer perception, a narrative intricately woven by decades of marketing strategies. Its seemingly simple composition belies a sophisticated marketing campaign that shapes how consumers view its nutritional value, often diverging significantly from the reality reflected in its nutritional profile.The marketing of American cheese frequently leverages imagery of convenience, family togetherness, and childhood nostalgia.
Advertisements often portray it as a versatile, quick, and readily available ingredient, implicitly minimizing its nutritional significance in favor of its practical utility. Product labeling, while legally obligated to provide nutritional information, often presents this data in a manner that is less prominent than the brand name or product image, subtly influencing consumer focus away from the details of its fat, sodium, and saturated fat content.
For example, a brightly colored package showcasing a smiling family enjoying a grilled cheese sandwich overshadows the smaller print detailing the grams of saturated fat per serving. This subtle manipulation of visual hierarchy influences the subconscious prioritization of convenience and appeal over nutritional awareness.
Discrepancies Between Perceived and Actual Nutritional Value, Nutrition facts american cheese
The disparity between consumer perception and the actual nutritional content of American cheese is significant. Marketing efforts often downplay the less desirable aspects of its nutritional profile.
- Perceived as a “mild” food: Many consumers perceive American cheese as a relatively light, low-calorie option, perhaps due to its pale color and smooth texture. However, a single slice often contains a substantial amount of saturated fat and sodium, significantly contributing to daily caloric intake.
- Association with childhood nostalgia: The sentimental connection to childhood often overshadows objective nutritional evaluation. The positive memories associated with grilled cheese sandwiches or macaroni and cheese can override a critical assessment of the food’s actual nutritional content.
- Emphasis on convenience and versatility: Marketing frequently highlights its ease of use and versatility in recipes. This focus on practicality often distracts from discussions about its nutritional impact within a balanced diet.
- Understated sodium content: The high sodium content of American cheese is often understated or indirectly presented in marketing materials. The focus remains on the taste and convenience rather than potential health implications related to high sodium intake.
Improving Nutritional Labeling for Enhanced Transparency
To bridge the gap between consumer perception and nutritional reality, improvements to American cheese packaging can foster greater transparency. Clearer, more prominent labeling is crucial.
“Nutritional information should be presented in a clear, concise, and easily understandable format, using simple language and visual aids.”
This includes:
- Larger font size for key nutritional facts: The number of calories, fat grams, saturated fat grams, and sodium milligrams should be prominently displayed in a larger font size than other information.
- Visual representation of nutritional content: Using simple charts or graphs to represent the percentage of daily recommended values for key nutrients can enhance consumer understanding.
- Contextualized information: Including information comparing the nutritional content to recommended daily allowances or similar products can help consumers make informed choices.
- Simplified language and clear explanations: Avoiding technical jargon and using straightforward language makes the nutritional information more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
FAQ Guide: Nutrition Facts American Cheese
Is American cheese good for you?
It depends! In moderation, it can be part of a balanced diet, but it’s high in sodium and saturated fat, so it’s not a superfood. Choose low-fat options if you’re watching your intake.
What are the best alternatives to American cheese?
Look for reduced-fat options or explore other cheeses like mozzarella, cheddar (in moderation!), or even some tasty vegan alternatives. Many offer similar melty goodness with better nutritional profiles.
Does American cheese have any vitamins?
Yes, it contains small amounts of vitamins like A and B12. However, don’t rely on American cheese as your primary source of these nutrients.
Is American cheese addictive?
While not technically addictive in the same way as drugs, its high sodium and fat content can contribute to cravings. Moderation is key!
